How to Strengthen HIPAA Compliance with Seven Core Practices?
Patient data is one of the most valuable assets in healthcare, and also one of the most vulnerable. Every record, message, and workflow involving Protected Health Information carries a level of responsibility that goes far beyond clinical care. For healthcare organizations, the challenge lies not only in protecting data but also in creating an environment where privacy, security, and accountability are part of daily operations.
HIPAA compliance influences how healthcare systems function across the board. It affects routine decisions, guides vendor selection, and shapes how teams communicate and collaborate. More importantly, it supports a culture of trust between providers and patients, ensuring that data is not only collected but also properly protected.
By using secure cloud infrastructure and HIPAA compliant hosting environments, organizations gain the flexibility to modernize without compromising on security. HIPAA compliance services provide the foundation for this transformation, helping healthcare teams stay ahead as threats grow more complex and regulatory expectations continue to rise.
How HIPAA Took Shape and Adapted?
Enacted in 1996, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) was introduced to improve insurance portability and bring consistency to how health information is handled. It built on earlier legislation like ERISA but addressed growing concerns around privacy and the increasing use of digital records.
Since then, HIPAA has evolved through amendments that strengthen privacy protections and reflect the healthcare industry’s shift to electronic systems and new care models. These changes ensure the framework remains relevant as technologies and data-sharing practices continue to develop.
How HIPAA Shapes Healthcare Behind the Scenes?
HIPAA compliance is often framed in legal or technical terms, but at its core, it is about trust. Patients trust that their information will be handled carefully, shared only when appropriate, and stored securely. HIPAA provides the framework for protecting sensitive data while helping healthcare systems operate with efficiency and transparency.
The foundation of HIPAA is the protection of Protected Health Information (PHI). This includes any detail that could identify a patient, such as names, addresses, medical records, insurance details, or visit dates. HIPAA defines how this information can be used and outlines the circumstances under which it may be disclosed, giving patients greater control over their own data.
HIPAA compliance goes beyond maintaining privacy. It requires healthcare organizations to preserve the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of PHI. In practice, this means keeping data secure from unauthorized access, ensuring its accuracy, and making it available when needed for treatment, billing, or coordination of care.
The regulation also promotes improvements within the healthcare system. By standardizing administrative functions such as electronic billing and data exchange, HIPAA helps streamline everyday processes. It also supports public health research and sets clear breach notification requirements, holding organizations accountable for non-compliance.
What HIPAA Aims to Achieve in Healthcare?
HIPAA plays a central role in shaping how health information is handled across the healthcare system. Its core functions are designed to safeguard patient rights, improve how data is shared, and support the secure exchange of electronic health records. Here are five key purposes that define HIPAA’s function:
-
- Encouraging Electronic Transactions: The law supports the secure and efficient transfer of data in processes like billing, claims submission, and eligibility verification. This improves turnaround times and reduces manual errors in administrative tasks.
- Building Public Trust in Healthcare: HIPAA empowers patients by granting access to their own health records and allowing them to request corrections. This transparency strengthens trust between individuals and their healthcare providers.
- Protecting Patient Privacy: HIPAA sets clear rules to ensure that PHI is handled responsibly. Covered entities, such as healthcare providers and insurers, must follow established standards to protect patient identities and sensitive medical details.
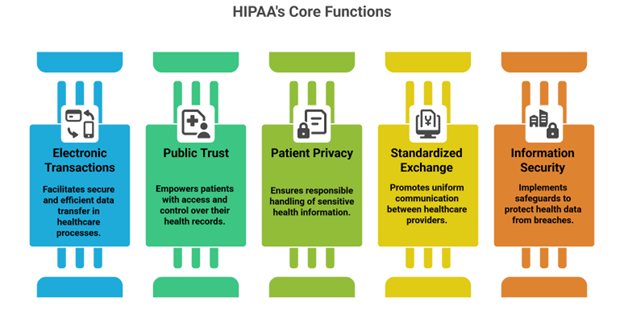
- Standardizing Health Information Exchange: HIPAA simplifies communication between providers by enforcing uniform formats for electronic data exchange. This reduces inconsistency and improves the reliability of shared records across different systems.
- Enhancing Security of Health Information: To reduce the risk of breaches or misuse, HIPAA requires organizations to implement administrative, physical, and technical safeguards. These measures help secure data from unauthorized access, loss, or tampering.
Together, these purposes make HIPAA not only a regulatory requirement, but a foundation for responsible and secure healthcare communication.
Seven Core Elements of an Effective HIPAA Compliance Program
For healthcare organizations, HIPAA compliance is more than a checklist. It requires a structured and accountable system that can withstand regulatory scrutiny. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) identifies seven essential elements that serve as the foundation of a strong compliance program. These components help shape internal processes and are used as benchmarks during audits by the Office for Civil Rights (OCR).
-
Written Policies and Standards of Conduct
Clear documentation of policies and conduct standards sets expectations for safeguarding health information and fulfilling HIPAA requirements.
-
Designated Compliance Officer and Committee
A responsible individual or team should be appointed to manage the compliance program and ensure all HIPAA policies are implemented and enforced.
-
Ongoing Training and Education
Regular training sessions help staff stay informed about HIPAA regulations and their specific responsibilities in maintaining compliance.
-
Clear Lines of Communication
Employees must have accessible channels to report concerns or violations without fear of retaliation. Transparent communication encourages early identification and resolution of issues.
-
Internal Monitoring and Auditing
Consistent monitoring allows organizations to detect potential compliance gaps and address them proactively. It also supports ongoing improvement.
-
Consistent Disciplinary Action
Enforcing disciplinary measures for noncompliance helps reinforce expectations and reduces the likelihood of repeated violations.
-
Timely Corrective Action
Organizations must act promptly when a breach occurs by investigating the cause, addressing deficiencies, and taking steps to prevent future incidents.
Avoidable HIPAA Missteps That Lead to Violations
Many HIPAA breaches stem from routine oversights rather than complex threats. Understanding the most common violations can help healthcare organizations take preventative action.
-
- Laptops, phones, and external drives that store PHI and are not encrypted can lead to serious breaches if lost or stolen.
- Throwing away paper records or digital media without using secure destruction methods puts sensitive information at risk.
- Accidentally sending PHI to the wrong recipient is a violation of HIPAA’s disclosure rules, regardless of intent.
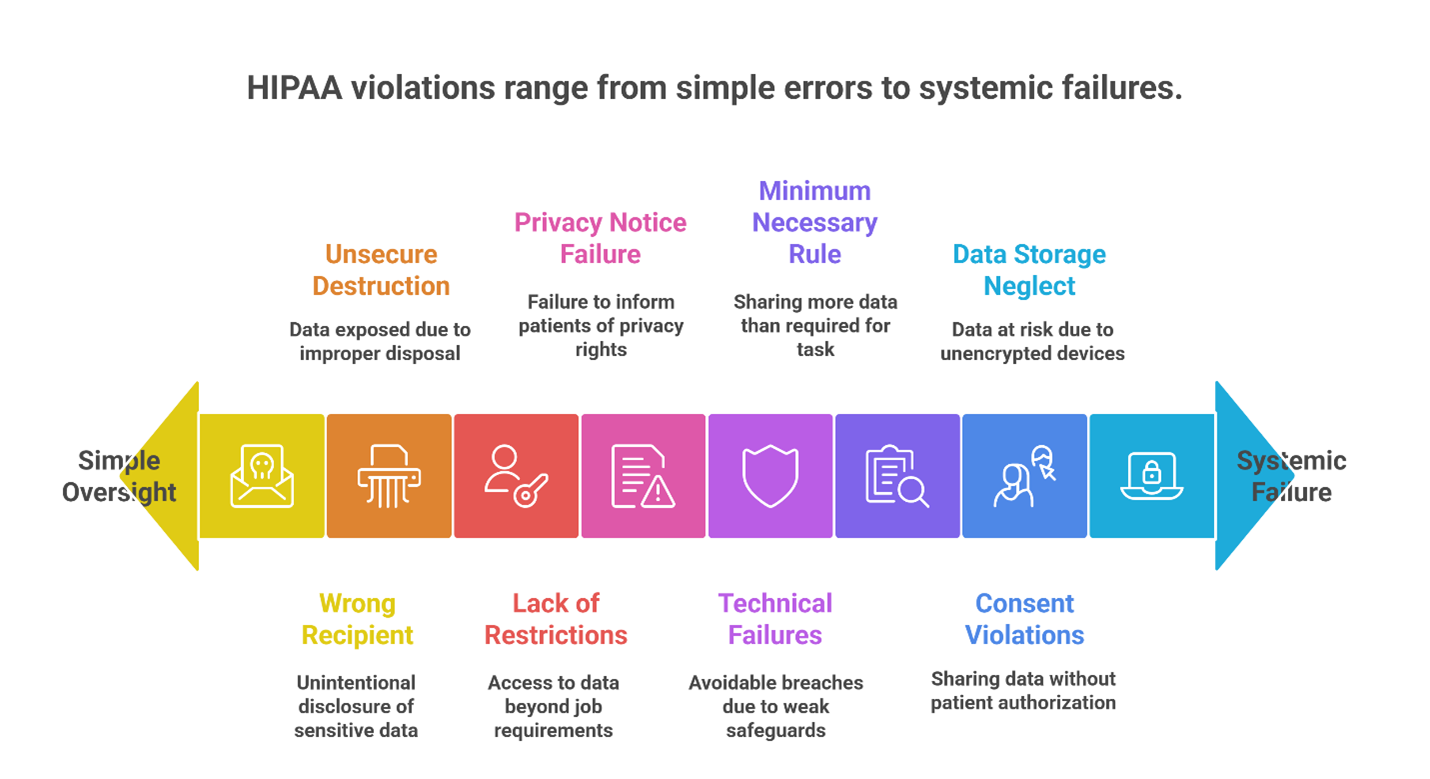
- Sharing PHI without proper consent or outside approved use cases compromises patient confidentiality.
- Viewing or distributing more PHI than necessary for a specific task violates the Minimum Necessary Rule.
- Without role-based access restrictions, staff members may access information they are not authorized to see.
- Failing to provide patients with a Notice of Privacy Practices or obtain their acknowledgment is a clear violation of HIPAA requirements.
- Inadequate technical, administrative, or physical protections can lead to breaches that are otherwise avoidable.
HIPAA Compliance Made Practical with Apps4Rent’s Microsoft 365 Solutions
HIPAA compliance is more than a legal obligation; it reflects a continued commitment to patient safety, operational integrity, and responsible data handling. To meet these expectations, healthcare organizations need a well-structured compliance approach that includes technical safeguards, employee training, and internal oversight.
As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, Apps4Rent supports healthcare providers in building secure, reliable IT environments that align with HIPAA standards. Our Office 365 plans can be designed to support HIPAA-compliant configurations, helping organizations enhance security while maintaining productivity and collaboration.
Beyond Microsoft 365, we also offer HIPAA-compliant mailbox solutions for organizations that require tighter control over healthcare communications. Whether you are upgrading your systems or strengthening existing infrastructure, our team ensures that compliance is built into every layer of your operations.
Apps4Rent helps reduce risk, meet regulatory requirements, and strengthen the trust of the patients and partners who depend on your services. Contact us today via chat, call, or mail to learn more.





